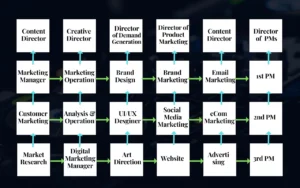
One such invaluable feature is the Jira Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), a crucial element for project managers aspiring to refine their project execution strategies.
Jira WBS allows teams to decompose the total scope of work into manageable sections, presenting a detailed view of project tasks and responsibilities, and enabling enhanced project control and clarity. Combining WBS principles with Jira’s features aids in precise project planning, task allocation, and monitoring.
Quickly explore Jira WBS for organized, efficient project management with this guide’s insights and practical knowledge. New to Jira or want to enhance its use? This guide shows how to effectively leverage Jira WBS for your projects.
Join us to explore Jira WBS nuances, empower your project management with actionable strategies, and deepen your understanding.
Understanding Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
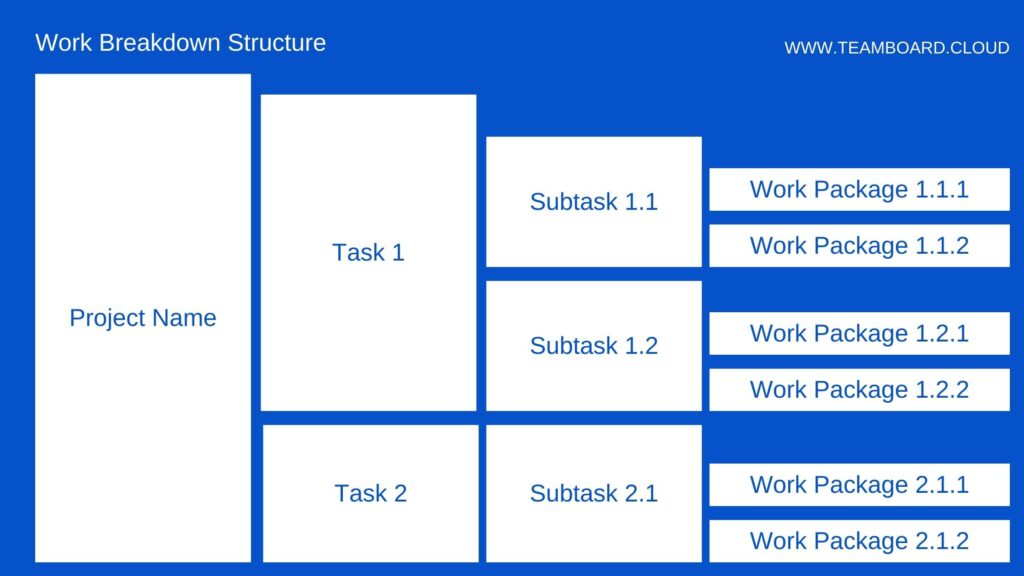
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a fundamental concept in project management, acting as a comprehensive map that delineates the scope and structure of the project. Hierarchical decomposition breaks down project work for team execution to achieve objectives and deliverables. Let’s delve deeper to understand the nuances of WBS and its significance in managing projects efficiently.
A. Origins and Development of WBS
The concept of WBS dates back to 1957, emerging as a crucial management tool during the development of the Polaris missile program. Since then, WBS has evolved, adapting to the needs of various industries and becoming a staple for project managers to visualize and define the detailed scope of work effectively.
B. Importance of WBS in Project Management
WBS is revered as the backbone of project planning, providing a clear and detailed structure of the project’s scope. It aids in:
- Defining clear project objectives: It lays out the tasks and subtasks clearly, avoiding ambiguity and scope creep.
- Resource Allocation: By breaking down tasks, WBS aids in the precise allocation of resources and assignment of responsibilities.
- Cost Estimation: It facilitates accurate estimation of costs associated with each task, allowing for effective budget management.
- Risk Management: A detailed WBS can help in identifying potential risks at an early stage, enabling proactive risk mitigation.
- Monitoring and Controlling: WBS serves as a foundation for project progress tracking and management, ensuring that the project stays on course.
C. Key Components of a Work Breakdown Structure
- Responsibility Assignment: Identifies the specific organization, department, or individual responsible for each segment of work, ensuring clarity in task delegation.
- Scheduled Dates: Includes the planned start and finish dates for each task, enabling meticulous timeline management.
- Resource Allocation: Outlines the resources needed for each task, facilitating optimal resource distribution and utilization.
- Cost Estimation: Provides an approximation of the project’s expense, allowing for effective budget planning and control.
- Charge Numbers: Allocates specific codes or numbers to different work packages for systematic tracking and billing.
- Contractual Information: Details the contract specifications, requirements, and milestones, ensuring compliance with contractual obligations.
- Quality Control Protocol: Defines the standards, requirements, and procedures to maintain the quality of work, minimizing errors and defects.
- Technical Requirements: Specifies the technical information and resources necessary to achieve the project goals, aiding in technical planning and management.
A Work Breakdown Structure is instrumental in dissecting a project into manageable parts, clarifying roles, responsibilities, and requirements. It plays a pivotal role in various aspects of project management, including scheduling, cost estimation, quality control, and resource allocation, enabling project managers to execute projects efficiently, control costs, maintain quality, and achieve successful project outcomes.
D. Who Uses Work Breakdown Structures?
Work Breakdown Structures (WBS) are used across various industries and professions due to their effectiveness in breaking down complex projects into manageable pieces. Here are some entities and professionals who commonly use Work Breakdown Structures:
Project Managers:
They use WBS to visualize the scope of the project, allocate resources efficiently, and monitor project progress. It allows them to identify potential risks early and make informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle.
Construction Industry:
Construction managers and engineers use WBS to detail construction phases, tasks, and subtasks, which aids in accurate estimations of cost, time, and resources and helps in managing complex construction projects effectively.
IT and Software Development Teams:
In software and IT project management, WBS is instrumental in outlining the development lifecycle, from conception to deployment, facilitating precise task delegation, timeline estimation, and progress tracking.
Event Organizers:
Event planners utilize WBS to break down the myriad components of event planning and execution, such as venue setup, catering, and entertainment, ensuring each element is thoroughly planned and executed.
Manufacturing Industry:
In manufacturing, WBS is used for product development and production processes, helping in detailing production phases, allocating resources, and monitoring production timelines and costs.
Research Teams:
Researchers and scientists use WBS to organize research projects, breaking down the research process into manageable tasks such as literature review, data collection, and analysis, to ensure systematic progress.
Aerospace and Defense Industries:
Given the complexity and precision required in these sectors, WBS is used extensively to detail every aspect of projects, from design to production to testing, ensuring meticulous planning and execution.
Healthcare Administrators:
Healthcare managers and administrators use WBS to manage healthcare projects and initiatives, breaking down tasks related to medical service improvement, facility management, and healthcare delivery optimization.
Government Agencies:
Government project managers utilize WBS to structure government projects and initiatives, ensuring organized planning, resource allocation, and execution of public service projects.
Education Administrators:
In the education sector, administrators and educators use WBS for planning and managing educational programs, curriculum development projects, and institutional initiatives.
Consultants and Analysts:
They use WBS to dissect projects into smaller tasks, aiding in the detailed analysis, planning, and implementation of solutions for their clients.
The versatility and applicability of Work Breakdown Structures make them a universal tool, embraced by various industries and professionals, aiming for meticulous planning, organized execution, and successful completion of their projects. Whether it’s developing a new software application, constructing a building, organizing an event, or undertaking a research project, a WBS can provide the structured framework needed to manage projects efficiently.
Integration with Jira
When integrated with Jira, WBS offers a more dynamic and interactive approach to project management. Jira WBS takes the structured decomposition of tasks provided by a traditional WBS and marries it with Jira’s user-friendly, agile environment, offering enhanced functionality such as real-time collaboration, tracking, and reporting, making it an indispensable tool for modern project managers.
Understanding WBS’s conceptual foundations and principles is pivotal for effective utilization of Jira WBS. It equips project managers with the knowledge to optimize the breakdown and allocation of tasks within Jira, ensuring a streamlined and organized approach to project completion.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into how to integrate and optimize WBS within Jira, exploring the practical applications and benefits of using Jira WBS for efficient and effective project management. Keep reading to discover how you can enhance your project management strategies by incorporating Jira WBS into your workflow.
Setting up Jira Work Breakdown Structure
Once you’re equipped with an understanding of WBS, implementing Jira WBS can significantly optimize your project management process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to setting up Jira Work Breakdown Structure efficiently:
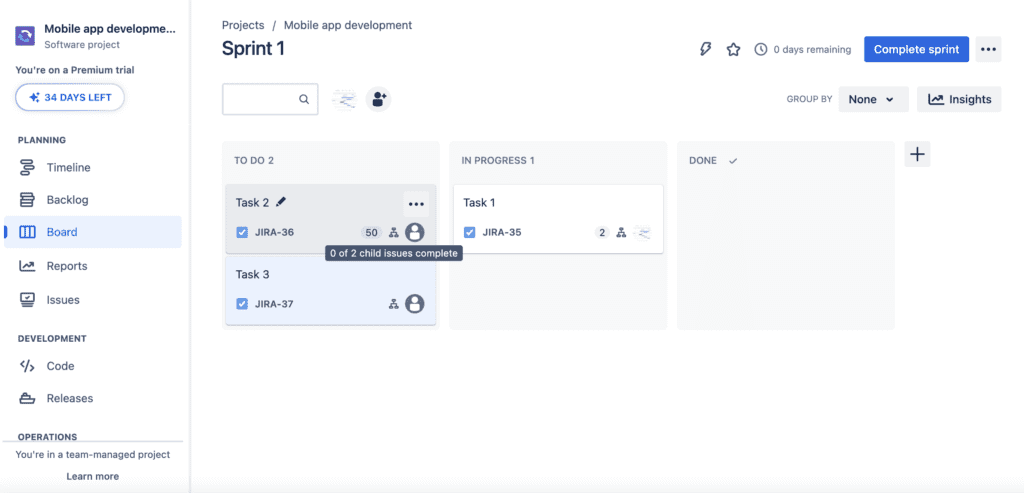
A. Preliminary Steps
- Creating a Jira Account: Before you can explore the functionalities of Jira WBS, you need a Jira account. Sign up on the official Jira website and choose a subscription plan that suits your needs.
- Setting up a Project: After logging in, create a new project by navigating to the ‘Projects’ tab. Select the project type and enter the necessary details.
B. Configuration and Customization
- Creating Issues and Sub-tasks: Within your project, create issues representing the main tasks, and then break them down into sub-tasks using the Jira WBS. This will help in defining the scope and sequence of the tasks efficiently.
- Configuring Fields and Screens: Customize the fields and screens as per your project needs. This can include adding, removing, or modifying fields for issues and sub-tasks to tailor the Jira WBS to your project’s requirements.
C. Visualization of WBS in Jira
- Using Different Plugins or Add-ons for Visualization: Explore and integrate plugins or add-ons available in the Atlassian Marketplace, such as the TeamBoard ProScheduler with WBS Gantt Chart for Jira feature, to visualize the breakdown of work and track the project’s progress effectively.
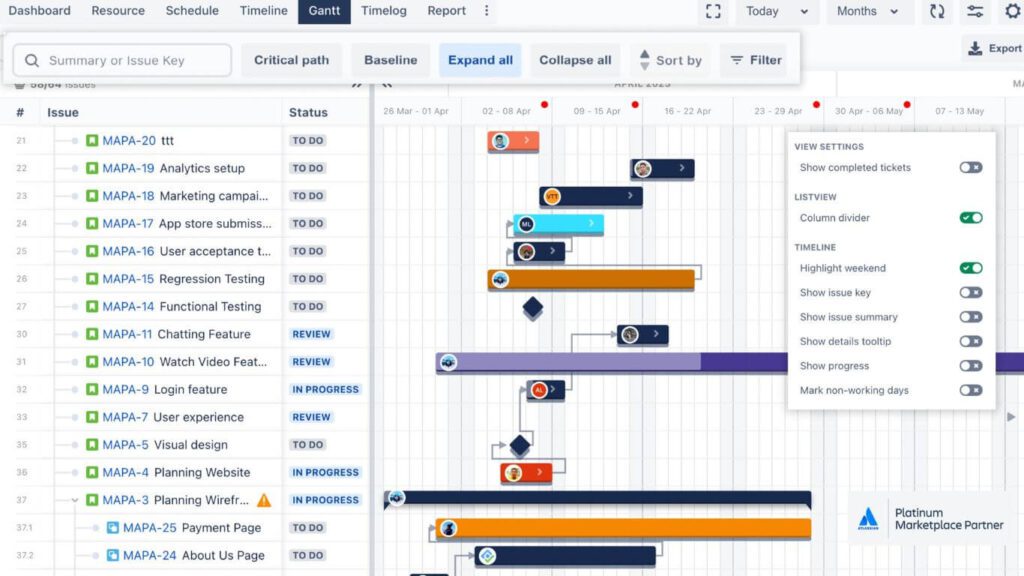
- Utilizing Jira’s Native Features for Visualization: Utilize the built-in features of Jira to create boards and charts, providing a visual representation of your project’s status and enabling easy monitoring of the progress.
Utilizing Jira WBS for Efficient Project Management
After setting up and configuring Jira WBS, optimizing its use is crucial for effective and efficient project management. Here, we delve into the various ways to utilize Jira WBS to ensure your projects run smoothly and successfully.
A. Assigning Tasks
- Utilizing Jira WBS, managers can assign tasks and subtasks to team members clearly and effectively, ensuring everyone knows their responsibilities.
- Setting Priorities: Tasks can be prioritized to guide team members on which tasks to tackle first, aiding in maintaining the project’s flow and ensuring critical paths are clear of blockages.
B. Monitoring Progress
- Tracking Logged Hours: Jira WBS allows for the logging of work hours on tasks and subtasks, providing insights into the time spent on different project elements and aiding in identifying any discrepancies in time allocation.
- Viewing Completed Tasks: Track the completion of tasks in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments to the project plan if necessary and ensuring the project stays on track.
C. Managing Resources and Budgets
- Resource Allocation: With Jira WBS, managers can allocate resources efficiently, balancing the workload among team members and preventing burnout.
- Budget Monitoring: Jira WBS enables close monitoring of project budgets, ensuring that the project stays within financial constraints and helping to identify any potential financial risks early.
Practical Tips for Optimizing Jira WBS
To get the most out of your Jira Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), you need to optimize its functionalities. Here are some practical tips and best practices that can help you use Jira WBS effectively.
A. Best Practices for Structuring WBS in Jira
- Develop a Detailed WBS: Start with high-level tasks and break them down into detailed sub-tasks.
- Use Consistent Naming Conventions: Establish and adhere to consistent naming conventions for tasks and sub-tasks.
- Set Clear Milestones: Define clear and achievable milestones within Jira WBS to keep the team motivated.
- Keep Tasks Mutually Exclusive: Ensure that tasks do not overlap in scope and are independent of each other.
B. Pitfalls to Avoid when Using Jira WBS
- Avoid Overly Complex Structures: Keep the WBS structure as simple and straightforward as possible. An overly complicated structure can lead to confusion and mismanagement.
- Do Not Neglect Regular Updates: Regularly update the WBS to reflect any changes in project scope, tasks, or timelines.
- Avoid Micromanagement: Monitor progress and allocate resources efficiently with Jira WBS, avoiding excessive project micro-management.
- Do Not Ignore Risk Management: Regularly assess and manage risks in Jira WBS for smooth project progression.
C. Recommendations for Efficient Use of Jira WBS
- Leverage Jira’s Advanced Features: Explore and use Jira’s advanced features to enhance WBS and boost project outcomes.
- Use Visual Representation: Use Jira’s visualization tools for clearer WBS representation and easier project data management.
- Keep Lines of Communication Open: Promote open team communication, addressing issues promptly with Jira’s WBS.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement:Seek feedback, learn from projects, and refine Jira WBS for improved management.
Conclusion
Jira WBS integrates task decomposition with a user-friendly environment, enhancing project management dynamically.
Jira WBS enhances organized, transparent project management with detailed task visualization, control, and optimized resource allocation.
Adopting Jira WBS can significantly elevate your project management practices, ensuring your projects are well-structured, monitored, and executed efficiently. It is highly encouraged for project managers aiming for successful project outcomes and enhanced team productivity.
Additional Resources
What is Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Gantt Chart
WBS Gantt Chart in Jira for Project/ Portfolio Management
WBS Gantt Chart in Jira using TeamBoard ProScheduler
Best Gantt Chart Integrations with Jira 2023
3 Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Gantt Chart examples for software development projects in 2023