Navigating the complexities of modern business demands a robust solution: enterprise resource planning (ERP). ERP systems act as the integrated backbone of a company, linking various departments and streamlining processes under one roof. As businesses seek greater clarity and coordination, the introduction of Jira for resource planning has become a game-changer.

This blog post will take you through the essentials of ERP and illustrate how Jira can simplify and enhance your enterprise’s resource planning efforts. With a focus on maximizing the efficiency and readability of information, we will uncover the strategic advantages of combining ERP with Jira’s dynamic capabilities. Whether you’re refining existing operations or building new frameworks, understanding ERP and Jira’s role is pivotal in today’s competitive landscape. Join us as we explore the intersection of these powerful tools.
Table of Contents
What is an enterprise resource planning (ERP)?
1. Definition of enterprise resource planning (ERP).
At its core, enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a system that integrates various functions into one complete, streamlined process. It allows for real-time management and analysis of business activities, facilitated by software and technology. An ERP system typically encompasses modules for finance, HR, manufacturing, supply chain, services, procurement, and others.
2. Historical Context
The concept of ERP dates back to the 1960s, with systems designed to monitor inventory. Over time, these evolved into Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems in the 1970s, which managed manufacturing processes, and further into MRP II in the 1980s, which included additional production resources. In the 1990s, the term ERP was coined to describe the broader suite of tools that manage not only inventory and production but all enterprise functions.
3. Key Components
ERP systems are built around a central database. This database ensures that the various departments within a business can access and rely on the same data for their specific needs. Key components include:
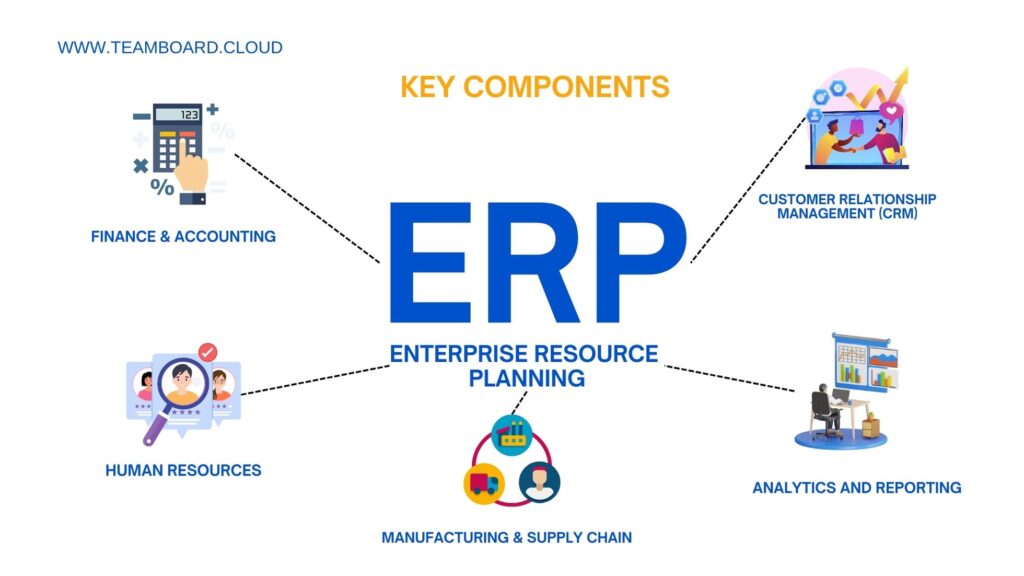
- Finance & Accounting: Tracks financial activities and generates reports on revenue, expenses, and profitability.
- Human Resources: Manages employee information, payroll, benefits, and recruitment.
- Manufacturing & Supply Chain: Controls production planning, inventory, procurement, and logistics.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Helps in managing customer information, sales pipeline, and customer service.
- Analytics and Reporting: Provides business intelligence that aids in decision-making.
4. Benefits of ERP
Implementing an ERP solution comes with a multitude of benefits:
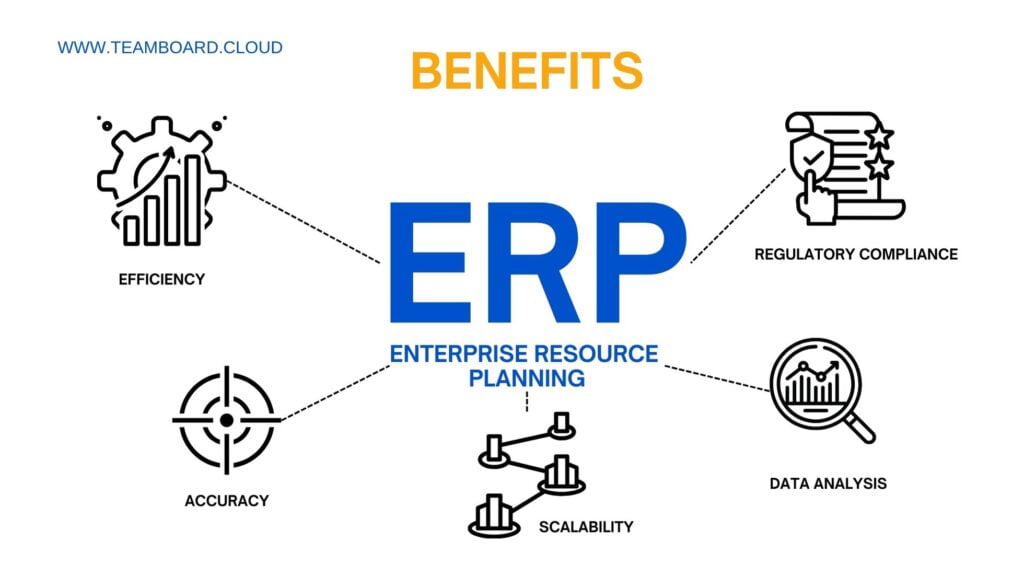
- Efficiency: By automating and streamlining business processes, ERP reduces manual labor and simplifies operations.
- Accuracy: Centralized data minimizes errors and ensures consistency across the organization.
- Scalability: ERP systems can grow with your business, accommodating new processes and additional data.
- Data Analysis: With integrated data, businesses can perform comprehensive analytics for better decision-making.
- Regulatory Compliance: An ERP system can help maintain compliance with industry and government regulations through built-in audit trails and reporting mechanisms.
5. Why ERP Matters
In the modern digital economy, ERP systems are not just a luxury, they are a necessity for businesses looking to remain competitive. They provide a 360-degree view of operations, help manage risks, and enable companies to quickly adapt to market changes or operational challenges.
The Role of ERP in Modern Enterprises:
Centralizing Business Operations
In today’s fast-paced business environment, ERP stands as a central nervous system for enterprises, channeling information and processes through one unified framework. It’s designed to centralize operations, making management of diverse business functions more cohesive and less siloed.
Enhancing Decision-Making
ERP systems provide leaders with a bird’s-eye view of their enterprise, offering insights that are pivotal for strategic decision-making. With data from every department at their fingertips, executives can make informed choices that align with the company’s overall objectives.
Driving Efficiency and Productivity
One of the most significant roles of ERP in modern businesses is its ability to drive efficiency. By automating routine tasks and reducing the need for manual input, ERP frees up employees to focus on more strategic, value-adding activities. This not only boosts productivity but also enhances job satisfaction among team members.
Facilitating Growth and Scalability
As businesses expand, the complexity of operations can increase exponentially. ERP systems facilitate growth by providing scalable solutions that can accommodate additional processes, products, and even acquisitions without disrupting the existing workflow.
Integrating Emerging Technologies
Modern ERP systems are often designed to integrate with emerging technologies such as IoT devices, AI, and blockchain. This integration allows businesses to stay at the forefront of innovation, leveraging new tools to enhance processes and gain a competitive edge.
Maintaining Compliance
With ever-changing regulations across industries, maintaining compliance can be a daunting task. ERP systems help enterprises stay compliant by providing tools to track and manage regulatory requirements, thereby reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Supporting Global Operations
For enterprises operating on a global scale, ERP systems are invaluable. They support multiple languages, currencies, and comply with various international regulations, enabling businesses to manage global operations seamlessly.
Impact of ERP on Culture and Workforce
The implementation of an ERP system can also influence corporate culture and workforce dynamics. It promotes a data-driven culture that values transparency and accessibility of information. For the workforce, ERP systems can mean enhanced collaboration, reduced frustration from disparate systems, and more opportunities for cross-functional learning.
Jira for Resource Planning
Jira, originally designed as a bug and issue tracker, has evolved into a robust work management tool. It’s utilized by teams not just in software development but across various departments to plan, track, and report on work. For resource planning, Jira’s flexible project management capabilities make it an invaluable asset.
Features of Jira Supporting Resource Planning
- Customizable Boards: Jira’s boards can be tailored to reflect all stages of resource planning, from initial requests to allocation and tracking.
- Workflows: Define processes that resources must go through, ensuring that nothing falls through the cracks and all compliance steps are followed.
- Real-Time Visibility: Teams have instant access to the status of resources, allowing for quick adjustments and forecasting.
- Advanced Reporting: Jira’s reporting tools provide insights into resource utilization, bottlenecks, and availability.
How Jira Revolutionizes Resource Planning for Agile Teams
Integrating Jira into ERP Systems
Jira can be integrated into a larger ERP ecosystem, providing a more agile layer focused on resource planning and tracking. The integration can harness the strengths of Jira in task management while benefiting from the centralized data and processes of an ERP system.
Customizing Jira for Enterprise Needs
- Plugins and Add-ons: Jira’s marketplace offers numerous plugins for enhanced resource planning, such as capacity planning and time tracking tools.
- Automation: Automate routine tasks within Jira to streamline the resource planning process.
- Permission Schemes: Control who can view and edit resource plans to ensure data integrity and security.
Jira’s Approach to Resource Management
- Task Assignment and Scheduling: Easily assign tasks to team members and schedule work based on availability and skill set.
- Time Tracking and Logging: Team members can log their time, providing clear data on resource expenditure.
- Capacity Planning: Forecast and plan for future projects based on current resource allocation and utilization.
Advantages of Using Jira
- Agility: Jira allows teams to adapt quickly to changes in priorities or demand.
- Transparency: With everything logged in Jira, team members and stakeholders can see the status of resources in real time.
- User-Friendly: Jira’s intuitive interface makes it easy for team members to manage their workloads and for managers to oversee resource allocation.
Challenges and Considerations
While Jira offers many benefits, there are considerations to keep in mind:
- Learning Curve: New users may need training to fully utilize Jira’s capabilities.
- Integration Complexity: Properly integrating Jira into an existing ERP system can require careful planning and execution.
Jira Resource Planning in Action
Setting Up Jira for Resource Planning
To harness Jira’s full potential for resource planning, a systematic setup is crucial. This includes:
- Defining Projects and Tasks: Organize your work into projects and further break them down into tasks or issues in Jira.
- Configuring Workflows: Customize workflows to mirror your resource planning and management processes, ensuring consistency and accountability.
- Allocating Resources: Use Jira to assign tasks to team members based on availability and skillsets, considering the balance and workload across the team.
Streamlining Resource Allocation
Jira simplifies the process of resource allocation with its visual interface, allowing planners to:
- Visualize Workloads: Utilize Jira’s dashboards to see who is working on what and who has capacity for more tasks.
- Balance Team Load: With Jira, you can ensure that work is evenly distributed, preventing burnout and underutilization.
Monitoring and Managing with Jira
The real-time monitoring features of Jira provide a dynamic way to manage resources:
- Tracking Progress: Monitor the status of tasks and projects, identifying any bottlenecks or delays.
- Adjusting Plans: Make real-time adjustments to resource allocations as project scopes evolve or unforeseen challenges arise.
- Reporting and Insights: Generate reports on resource utilization, project progress, and more, to inform future planning.
Customizing Jira for Different Enterprise Needs
Jira’s versatility comes from its customization options:
- Adding Fields and Screens: Add custom fields to capture specific information about resource planning within your organization.
- Creating Dashboards: Build dashboards that provide key stakeholders with a snapshot of resource allocation and availability.
Leveraging Jira Add-Ons
The Atlassian Marketplace offers a variety of add-ons to extend Jira’s resource planning capabilities:
- TeamBoard TimePlanner: Time Tracking, TimeSheet and Resource management
- TeamBoard ProScheduler: Scheduling Task, Project Management, Gantt Chart
- Tempo Timesheets: For time tracking and reporting.
- BigPicture: For managing and visualizing cross-project resource allocation.
- eazyBI Reports and Charts: For advanced analytics and reporting.
Jira as a Collaborative Tool
Jira encourages collaboration by:
- Commenting and Sharing Files: Team members can comment on tasks and share files directly within Jira, keeping all relevant information in one place.
- Integrating with Confluence: Combine Jira with Confluence to create a comprehensive knowledge base linked directly to your resource planning activities.
Optimizing Resource Planning with Jira
To optimize resource planning, consider:
- Regular Reviews: Regularly review resource allocations and project progress to identify areas for improvement.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop with team members to continuously refine the resource planning process.
Comparing Jira with Other ERP Tools:
When it comes to resource planning, Jira stands out for its agility and adaptability, but how does it compare to more traditional ERP tools? Here’s an analysis:
Flexibility vs. Comprehensive Integration
- Jira: Offers a high degree of flexibility, allowing teams to adapt quickly to project changes. It’s particularly strong in areas requiring agile project management.
- Traditional ERP: Provides comprehensive solutions that integrate a wide range of business processes, from finance to supply chain management.
User Interface and Experience
- Jira: Known for its user-friendly interface, Jira is designed to facilitate collaboration and ease of use for team-based projects.
- Traditional ERP: ERP interfaces can be more complex due to the breadth of functionalities, which may require more extensive training for users.
Customization and Scalability
- Jira: Highly customizable through add-ons and plugins. It can scale with the needs of the team or project.
- Traditional ERP: While ERP systems are scalable to handle increased organizational demands, customization can be more complex and often requires vendor support.
Cost Considerations
- Jira: Generally offers a lower entry cost, with flexible pricing models based on team size and selected features.
- Traditional ERP: Implementing an ERP system can be a significant investment, with costs associated with licensing, implementation, training, and maintenance.
Implementation Timeframe
- Jira: This can be rolled out relatively quickly, especially for teams familiar with agile methodologies.
- Traditional ERP: Implementation can take a significant amount of time, often requiring a tailored setup and company-wide training.
Resource Planning Specifics
- Jira: Excelling in project and task-level resource planning, Jira is well-suited for managing timelines, backlogs, and team workloads.
- Traditional ERP: Focuses on broader resource planning, including financial resources, human capital, inventory levels, and equipment.
Integration Capabilities
- Jira: While Jira can integrate with various systems, it is typically best paired with other Atlassian products or those available in the Atlassian Marketplace.
- Traditional ERP: Designed to be the central hub of all enterprise data, ERP systems often offer extensive integration capabilities with other enterprise-level systems.
Reporting and Analytics
- Jira: Provides robust reporting features for project management, but requires add-ons for more advanced analytics.
- Traditional ERP: Usually includes powerful built-in analytics and reporting modules that can handle complex data from across the enterprise.
In closing, the synergy between enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and Jira offers businesses a comprehensive approach to managing their operations. ERP provides the overarching structure necessary for integrating all business processes, while Jira brings agility and fine-tuned control to project and resource management.
As we’ve explored their distinct and intersecting roles, it’s clear that the choice between them—or the decision to use them in tandem—should be tailored to your organization’s specific needs and strategic objectives.
Adopting these tools can lead to enhanced efficiency, clearer communication, and improved productivity, ultimately driving your business forward. As you reflect on the insights shared, consider how these solutions can be part of your enterprise’s growth story. The path to optimized resource planning and project success is multifaceted, and with tools like ERP and Jira, you’re well-equipped to navigate it with confidence.